Virtual Reality (VR) is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in today's business landscape, redefining the way companies interact with customers. Moving far beyond its origins in gaming, VR is revolutionizing business engagement strategies across various sectors.
With the VR market projected to reach $12.1 billion by 2024, its integration into business operations has become a critical move for forward-thinking companies.
This article explores the extensive impact of VR across different industries, showcasing its potential to significantly reshape customer experience.
1. The Evolution of VR and Customer Interaction

VR technology has evolved from a niche gaming accessory to a mainstream business tool. The advancements in VR hardware, making it more affordable and user-friendly, have democratized its access.
This evolution is revolutionizing customer interaction, offering immersive experiences that bridge the gap between digital convenience and physical realism.
Now, industries ranging from healthcare to education are adopting VR to enhance their services and offerings.
This widespread adoption underscores VR's versatility and its ability to create deeply engaging and memorable experiences that resonate with users across various contexts.
2. VR Transforming Retail and E-Commerce
In the retail and e-commerce sectors, VR is a game-changer. Imagine walking into a virtual store from the comfort of your home, trying on clothes, or checking out gadgets in a 3D environment. This is no longer science fiction.
For instance, Tommy Hilfiger introduced VR headsets in their stores, allowing customers to experience a 360-degree fashion show. This immersive experience led to a 19% increase in sales.

Similarly, in e-commerce, Shopify reported that interactions with 3D/VR content showed a 94% conversion rate increase.
Another example is IKEA's VR kitchen experience allows customers to virtually remodel their kitchens, choosing cabinets and appliances, and even simulating cooking.
These examples underscore VR's potential in bridging the gap between online and in-store experiences, offering customers a unique and engaging shopping journey.
3. VR in Service and Support
VR's application extends to customer service and support, providing innovative solutions to traditional problems. Remote assistance through VR enables experts to guide customers through complex setups or troubleshooting as if they were present in the same room.
For example, Audi uses VR to provide customers with a detailed, interactive guide to their car, allowing them to understand features and troubleshoot issues in a virtual environment.
This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces the time and cost associated with in-person support.
4. VR in Product Development and Testing
Cost-Effective and Efficient Prototyping:
- VR allows for the creation and testing of virtual product models.
- Reduces the need for costly physical prototypes.
- Facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling quicker iterations and faster product development cycles.
Identifying Design Flaws and Improvements:
- Enables early detection of design issues or potential enhancements.
- Facilitates iterative design processes in a virtual environment.
- Enhances the accuracy of design assessments, leading to better-informed decisions and product refinements.
Example of Automotive Industry Application:
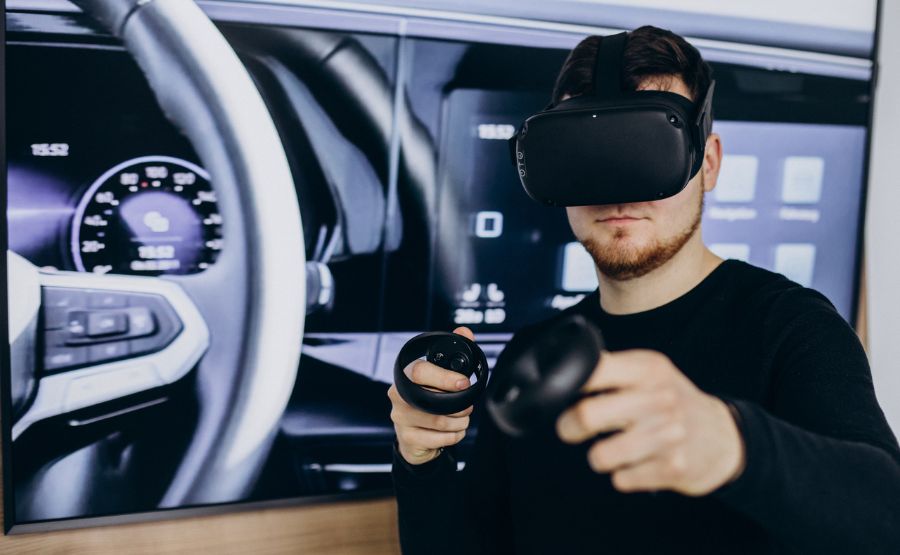

- Ford and Hyundai utilize VR for vehicle design and testing.
- Engineers and designers collaborate in VR, streamlining the development process.
Benefits of VR in Product Development:
- Accelerates the development timeline.
- Reduces overall production costs.
- Enhances the quality of the final product.
- Promotes environmental sustainability by reducing the need for physical materials.
5. Enhancing Customer Engagement through Gamification
Gamification, the incorporation of game-like elements in non-gaming contexts, is another area where VR is making a significant impact. By gamifying customer experiences, businesses can increase engagement and foster deeper brand loyalty.
For instance, Marriott’s VR Postcards offer immersive travel experiences to users, transporting them to exotic locations.
This not only entertains but also creates an emotional connection with the brand, encouraging repeat business and referrals.
6. The Future of VR in Customer Experience
The future of VR in customer experience is laden with potential. The integration of VR with AI and IoT is set to create more personalized and interactive experiences.
For instance, AI can tailor VR experiences to individual preferences, while IoT can provide real-time data to enhance VR environments.
The potential for VR in customer experience is vast, with applications ranging from virtual try-ons in fashion to immersive property tours in real estate.
Its ability to create immersive, engaging, and interactive experiences is unmatched. Businesses embracing VR technology are not only staying ahead of the curve but also setting new standards in customer engagement.
The era of VR in customer experience is here, promising to transform business interactions and create memorable, revolutionary experiences for customers.









Virtual Reality: The Next Frontier in Customer Experience
Virtual Reality (VR) is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in today’s business landscape, redefining...
Share this link via
Or copy link